Jeremy’s IT Lab lecture video:
Commands
Commands List
DHCP Snooping Show Commands
21. DHCP Snooping
Link to original
- show ip dhcp snooping binding
-->Shows the DHCP snooping binding tableDHCP Snooping Global Commands
ErrDisable (Port Security / DHCP Snooping / ARP Inspection)
Link to original
- errdisable recovery cause cause { psecure-violation | dhcp-rate-limit | arp-inspection }
-->Enables err-disable recovery for the specified cause- errdisable recovery interval seconds
-->Determines how long the switch should wait before enabling an err-disabled interface (if the err-disable recovery for that cause is enabled)DHCP Snooping Global
Link to original
- ip dhcp snooping
-->Enables the DHCP snooping functionality on the switch (needs to be enabled per VLAN as well)- ip dhcp snooping vlan vlan-id
-->Enables DHCP snooping on the specified VLAN- no ip dhcp snooping information option
-->Disables applying Option 82 for DHCP messagesDHCP Snooping Interface Commands
DHCP Snooping Interface
Link to original
- ip dhcp snooping trust
-->Configures the current interface as trusted for DHCP snooping- ip dhcp snooping limit rate packets-per-second
-->Limits how many DHCP packets are allowed per second
DHCP Snooping Info
DHCP Snooping General Information
DHCP snooping is a security feature of switches that is used to filter DHCP messages received on untrusted ports. It only filters DHCP messages, anything else is not affected.
- By default, all ports are untrusted. There’s also a standard to follow while assigning trusted ports.
- Uplink ports are configured as trusted ports. (The ports pointing towards network devices)
- Downlink ports are configured as untrusted ports. (The ports pointing towards end hosts)
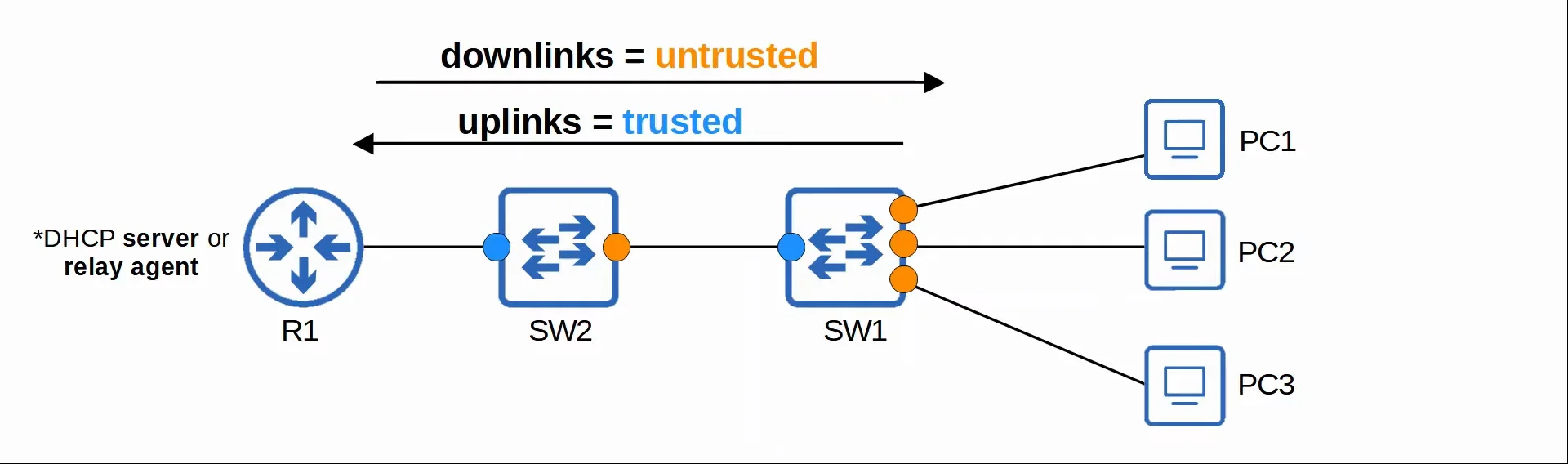 |
|---|
| Uplinks and Downlinks |
Example Attacks
1. DHCP Exhaustion/Starvation
An example of a DHCP-based attack is DHCP Exhaustion/Starvation.
- An attacker uses spoofed MAC addresses to flood DHCP Discover messages with unique CHADDRs (Client Hardware Address, which indicates the MAC address of the client).
- This leads to the target’s DHCP pool to become full, resulting in a DoS.
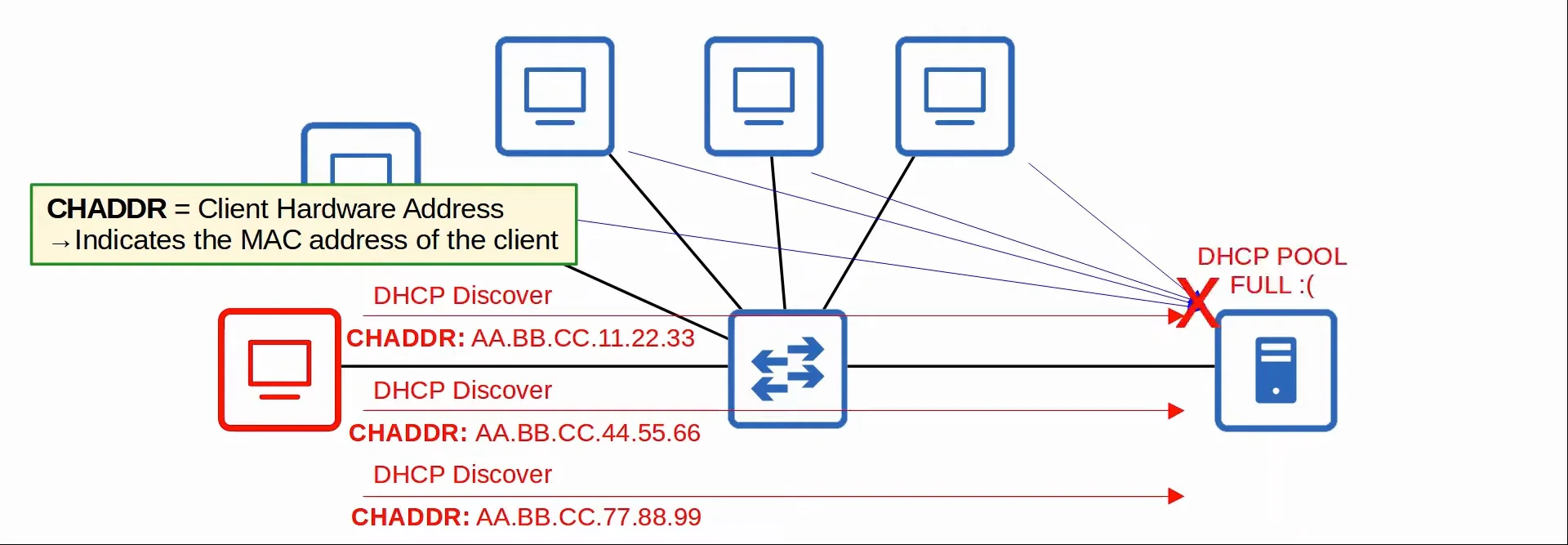 |
|---|
| DHCP Exhaustion/Starvation Demonstration |
2. DHCP Poisoning (Man-in-the-middle)
DHCP Poisoning is similar to ARP Poisoning. It can be used to perform a man-in-the-middle attack.
- A spurious (malicious) DHCP server replies to clients’ DHCP Discover messages and assigns them IP addresses, but makes the client use the spurious server’s IP as the default gateway.
- (Clients usually accept the first DHCP Offer message they receive)
- This will cause the client to send traffic to the attacker instead of the legitimate default gateway of the network.
- The attacker can then examine/modify the traffic before forwarding it to the legitimate default gateway.
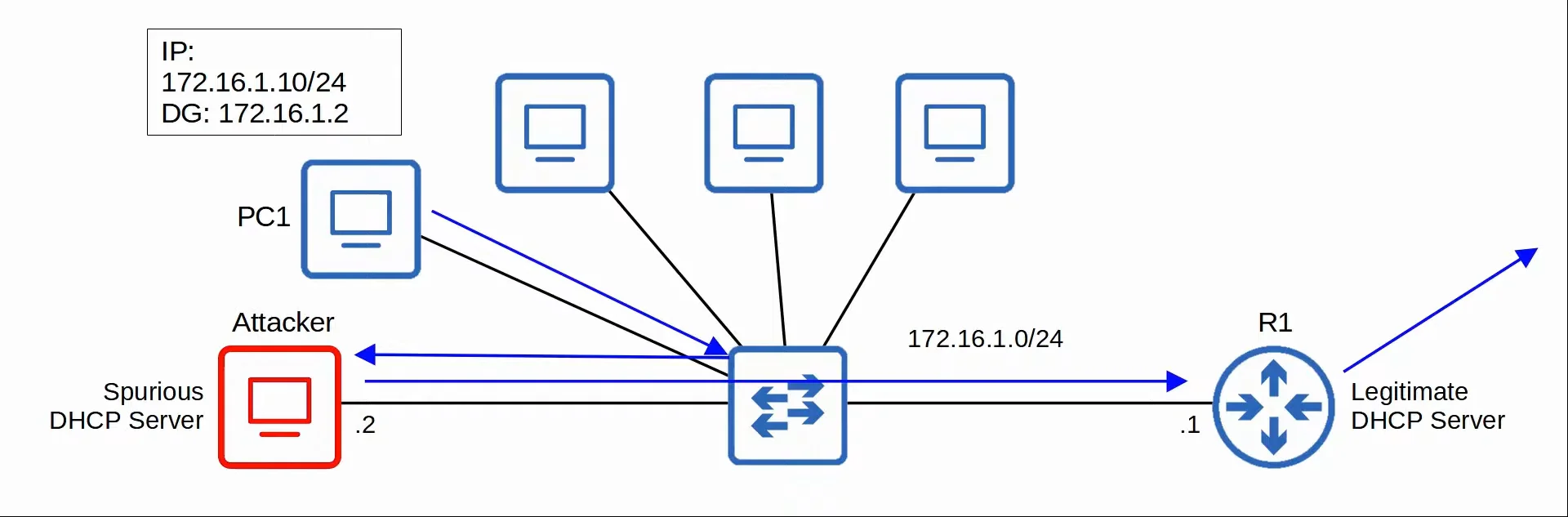 |
|---|
| DHCP Poisoning Demonstration |
DHCP Message Types
There are two types of DHCP messages, DHCP Server messages and DHCP Client messages.
- DHCP Server
- Offer
- ACK
- NAK (Opposite of ACK, used to decline a client’s DHCP Request)
- DHCP Client
- Discover
- Request
- Release (Used to release a client’s IP address)
- Decline (Used to decline the IP address offered by a DHCP server)
DHCP snooping has the ability to differentiate and filter between both of them.
DHCP Snooping - Configurations
show ip dhcp snooping binding- Shows the DHCP snooping binding table
- Includes information such as:
- MAC Address
- IP Address
- Lease time
- Type
- VLAN
- Interface
ip dhcp snooping- Enables the DHCP snooping feature globally to be used on the switch.
ip dhcp snooping vlan VLAN-ID- Enables DHCP snooping on a specific VLAN.
ip dhcp snooping trust- Configures the current interface as a trusted DHCP snooping interface.
ip dhcp snooping limit rate PACKETS-PER-SECOND^dhcp-snooping-limit-rate- Limits how many DHCP packets are allowed per second.
no ip dhcp snooping information option- Disables applying Option 82 for DHCP messages.
- (What is Information Option 82?)
errdisable recovery cause dhcp-rate-limit- Enables err-disable recovery for DHCP snooping rate limits.
DHCP Snooping - Operations
- When a client successfully leases an IP address from the DHCP server, create a new entry in the DHCP snooping binding table.
- If a DHCP message is received on a trusted port, forward it as normal without inspection.
- If a DHCP message is received on an untrusted port, examine it and act as follows:
- If it’s a DHCP Server message:
- Discard the message.
- If it’s a DHCP Client message, perform the following checks:
- Discover/Request:
- Check if the frame’s source MAC address and DHCP message CHADDR fields match or not.
- Match = Forward
- Mismatch = Discard
- Release/Decline:
- Check if the packet’s source IP address and the receiving interface match the entry in the DHCP snooping binding table.
- Match = Forward
- Mismatch = Discard
- Discover/Request:
- If it’s a DHCP Server message:
DHCP Snooping - Rate-Limiting
- Limits how many DHCP packets are allowed per second.
- DHCP Rate-limiting is disabled on all interfaces by default.
- If the rate of DHCP messages goes over the configured limit, the interface goes into err-disabled mode.
- The rate can be configured through the ip dhcp snooping limit rate PACKETS-PER-SECOND command.
- Can be re-enabled with
shutdown⇒no shutdown, or through ErrDisable Recovery (errdisable recovery cause dhcp-rate-limit).
DHCP Snooping - Option 82 (Information Option)
- Option 82, also known as the ‘DHCP relay agent information option’ is one of many DHCP options. It is usually used when there’s a remote DHCP server.
- DHCP relay agents can add Option 82 to messages they forward to the remote DHCP server.
- It provides additional information about which DHCP relay agent received the client’s message, on which interface, in which VLAN, and etc.
- It can be disabled with
no ip dhcp snooping information option - When DHCP snooping is enabled, by default Cisco switches will add Option 82 to DHCP messages they receive from clients, ==even if the switch isn’t acting as a DHCP relay agent==.
- By default, Cisco switches will drop DHCP messages with Option 82 that are received on an untrusted interface.
- Also by default, Cisco routers will drop DHCP messages with Option 82 that haven’t been sent by a DHCP relay agent.
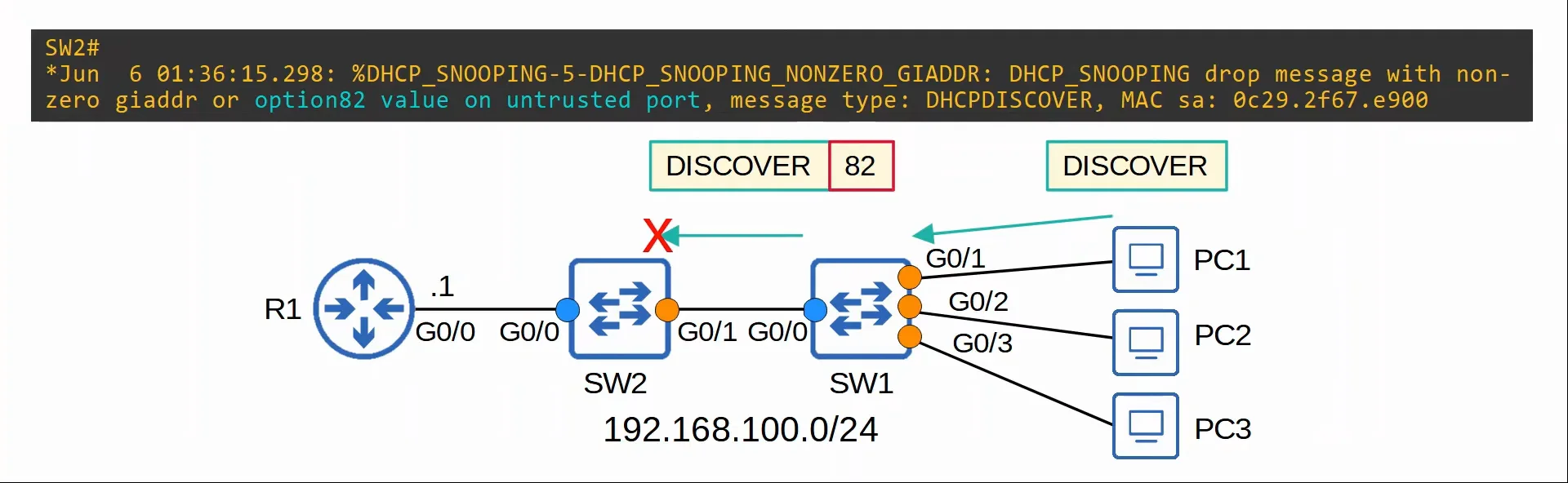 |
|---|
| DHCP snooping on a Cisco switch blocking an Option 82 message. |
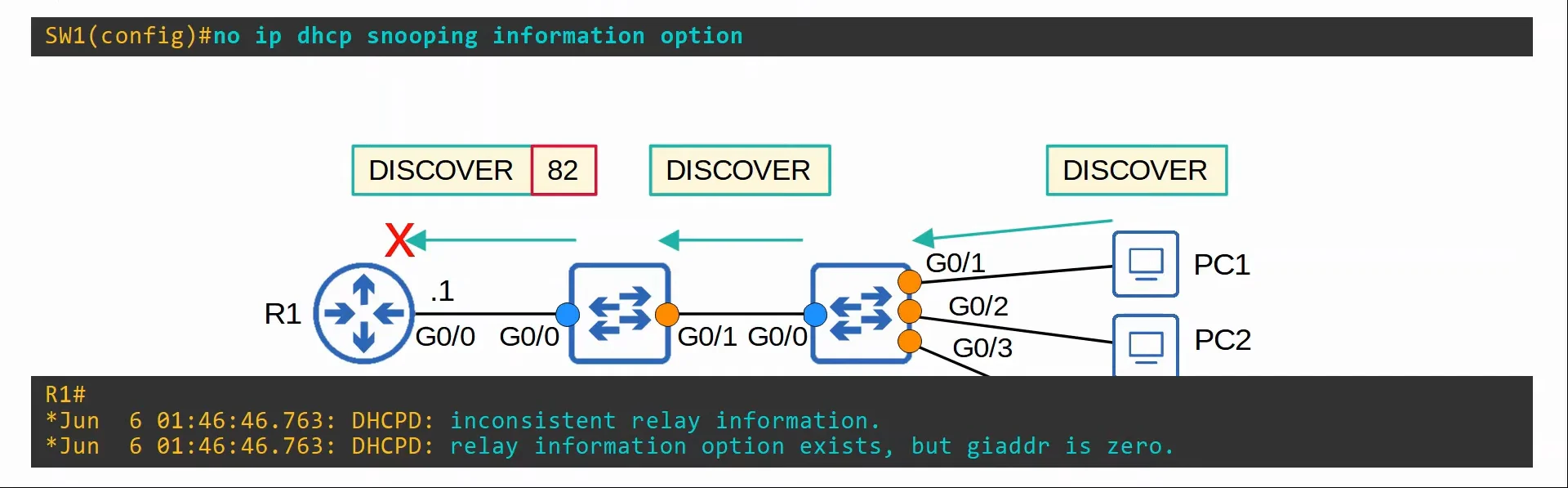 |
|---|
| Cisco router blocking an Option 82 message that didn’t arrive from a DHCP relay agent. |